本站已运行

-
作者: 宅男女神
查看: 6249|回复: 20
more +今日重磅推荐Recommend No.1
more +社区更新Forums
- 2015最新乾颐堂CCIE DC V2马海波数据中心课程四门全套
- 【新盟教育】有了这套视频不愁学不会Linux【0基础入门必看!】
- 鸟哥的Linux私房菜
- 鸟哥的Linux私房菜-基础篇.第四版(带书签)2021.06.12更新链接
- CCDA自学指南-设计Cisco互连网络解决方案
- 思科模拟器CiscoPacketTracer822,带汉化文件,亲测好用。
- 北京ccie考场现场照片....图片来自网上收集 免费 回帖可见
- 13G Wolf 最新版 CCIE RS 培训视频 含独有实验 完整版 一次学完思科网络技术课程
- BGP视频教程 路由抑制视频 SUPPER-MAP试验视频 LP 配置视频
- 2015王达老师《H3C交换机配置与管理完全手册(第二版)》电子书
more +随机图赏Gallery
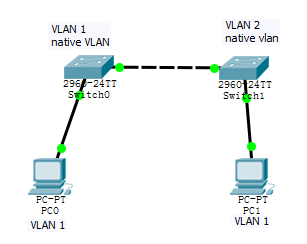
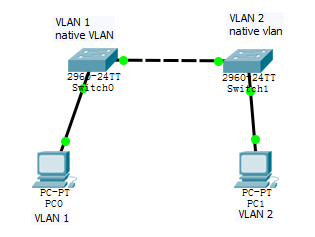
[求助] 悬赏500金币 彻底搞懂native vlan不一致的问题 看看这两个pc到底能不能通?na题库变种 |
| |
评分 | |
| |
| |
| |
| |
评分 | |
| |
| |
| |